Are you done implementing all the SEO strategies and still seeing no difference in the ranking? It’s time to roll up your sleeves and head towards website audit to check for technical errors. Without much ado, let’s get started with a comprehensive website audit guide.
But before that, please note the mentioned steps will familiarize you with the whole process in an introductory manner. Later, after finishing your first website audit, you may also dig deeper to know the minute details.
Headsup – it might look overwhelming, so remember to follow one step at a time.
What is a Website Audit?
A website audit is like checking how well your webpage is doing before making significant changes for better search engine results or redoing the site. By auditing, you can find out if your website is set up to get the traffic you want and get ideas on improving it to reach those goals.
What are the types of Website audits?
There are six types of Website Audits–
- Competitive Website Audit – A competitive website audit monitors competitors’ online activities. It helps you spot opportunities that your brand might be overlooking.
- Links Audit – Link audits check the web address source, domain, and anchor text to see if your page gets value and equity (“link juice”). This audit looks at the links to your website to identify any problems or chances for improvement in your backlink profile. By assessing your links, this audit will assist in making your site better for ranking with your desired keywords.
- Conversion Audit – A lead conversion optimization audit looks into a website’s conversion problems and chances for improvement. In this audit, you’ll need to check how visitors reach your website and where they’re coming from.
- Social Media (SM) Audit – Check each account to ensure they match the company’s branding, using the same images, logo, and tone of voice. Also, assess how well each page is doing. Then, use what you learn to understand your audience better and improve your social media to engage with them.
- SEO Website Audit – SEO Website Audit includes links and things like how you use keywords, your content, metadata, page speed, user experience, and video optimization. You can do an SEO audit independently, but hiring an agency might provide more thorough answers in less time. To perform an SEO website audit, check all your website pages. Use tools for website audit to assess various SEO metrics, such as crawling, indexing, security, usability, and other technical issues that might affect your site’s ranking in search results.
- Data Privacy (Audit) – A data privacy audit checks if you follow the right privacy laws and make a secure environment for website visitors. Search engines check for pages about privacy to decide if a website is trustworthy.
A Website Audit Checklist Prerequisite tools for conducting a complete Site Audit, Page Audits etc.
- Content Management System (CMS): To access the backend of your website (like WordPress etc.)
- A mobile device: To conduct some manual testing as part of the audit.
- Google Analytics: To identify pages to audit based on traffic and goal performance. It takes about a month for Google to collect data.
- Google Search Console (GSC) is essential for content and technical SEO audits. Use it to request reindexing, submit sitemaps, and more.
- Page speed calculators: Google’s PageSpeed Insights and GTMetrix are helpful tools.
- Image compressor: Use tools like Tinypng.com or themeisle.com for compressing images.
- SEO software: If you want deeper SEO metrics (like backlinks, competitive information, and keyword data), use Ahrefs, Moz Pro, Screaming Frog, SEMrush, etc. Some offer free trials or services for a limited number of links.
- Accessibility audit tools: Tools like WAVE or webaccessibility.com can help in this audit.
- Website graders: Grader tools provide guidance and simplify results. For non-SEOs, they can explain what the results mean.
How to do a Website Audit?
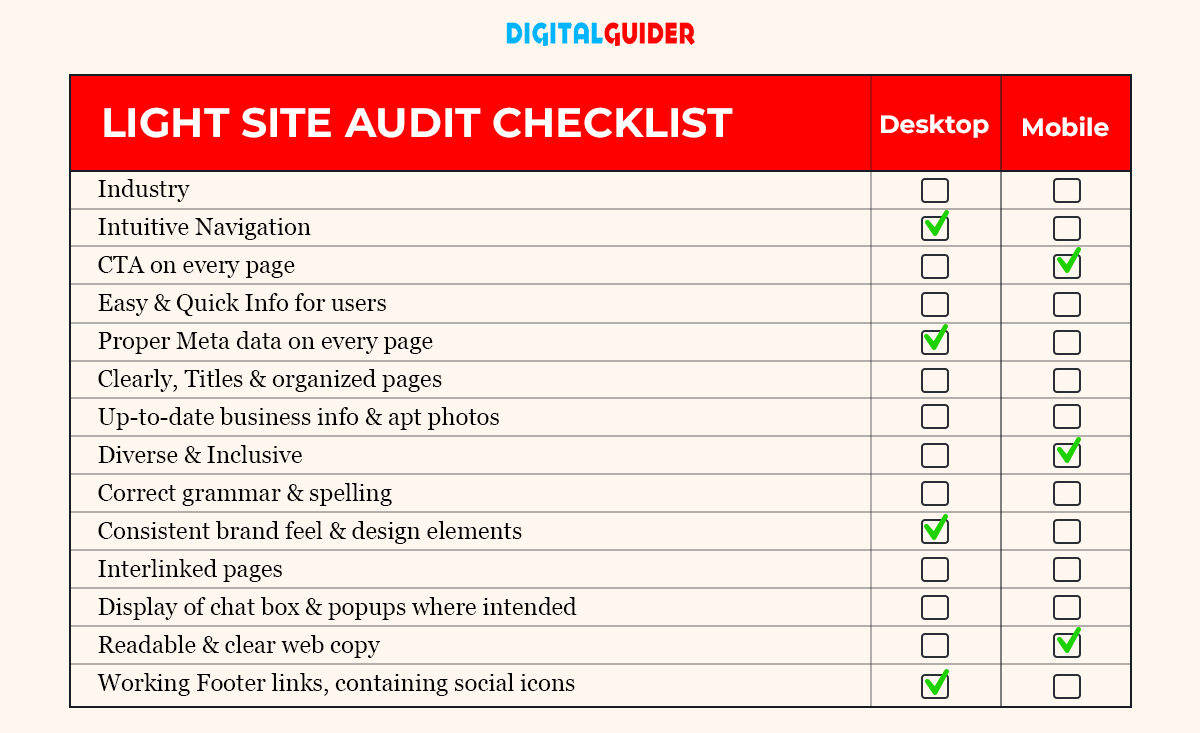
1— The First Step Towards Website Audit: Keep it Light
This audit is applied to your website’s core pages and covers each SEO category at a surface level. In other words, this kind of investigation requires you to check the ‘home’ page, ‘services’ page/’products,’ ‘about us,’ ‘contact us’ pages, blog post, 404 error page, navigation, etc. It also helps you to get away with minor issues and errors quickly. The focus here is on apparent errors, first impressions, accuracy of business information, and branding.
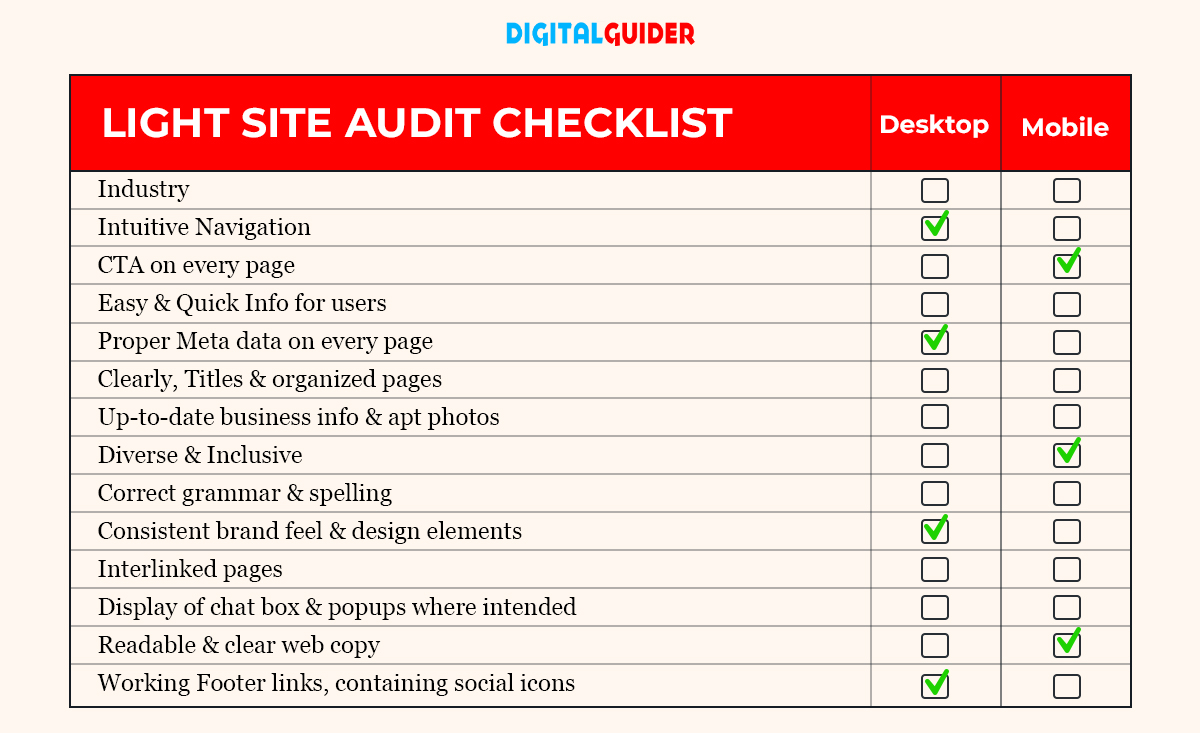
Don’t fret if your blog or website content is buried in the depth of the search results. Instead, start making the existing content SEO-friendly, fresh & reliable by following the below checklist.
Here is a checklist for starting a light SEO audit –
-
Your website should clearly show what your business is about.
-
Make sure people can easily navigate through your site.
-
Every page should encourage users to take action.
-
Important information should be easy to find.
-
Ensure each page has a good title and description.
-
Organize information and give pages clear titles.
-
Keep business details and photos accurate.
-
Include diverse photos and graphics of people.
-
Check for proper spelling and grammar.
-
Maintain a consistent design and brand feel.
-
Make sure pages are interconnected.
-
Popups and live chat should appear only when necessary.
-
Make website copy friendly, readable, and transparent.
-
Ensure footer links work and include social icons.
After conducting a light SEO audit, the different massive pieces come next. Majorly, SEO comprises On-page SEO, Off-page SEO, and Technical SEO. Depending upon your services, it can include other SEOs like Local SEO, International SEO, etc.

Let’s dive into the first significant chunk of the SEO family.
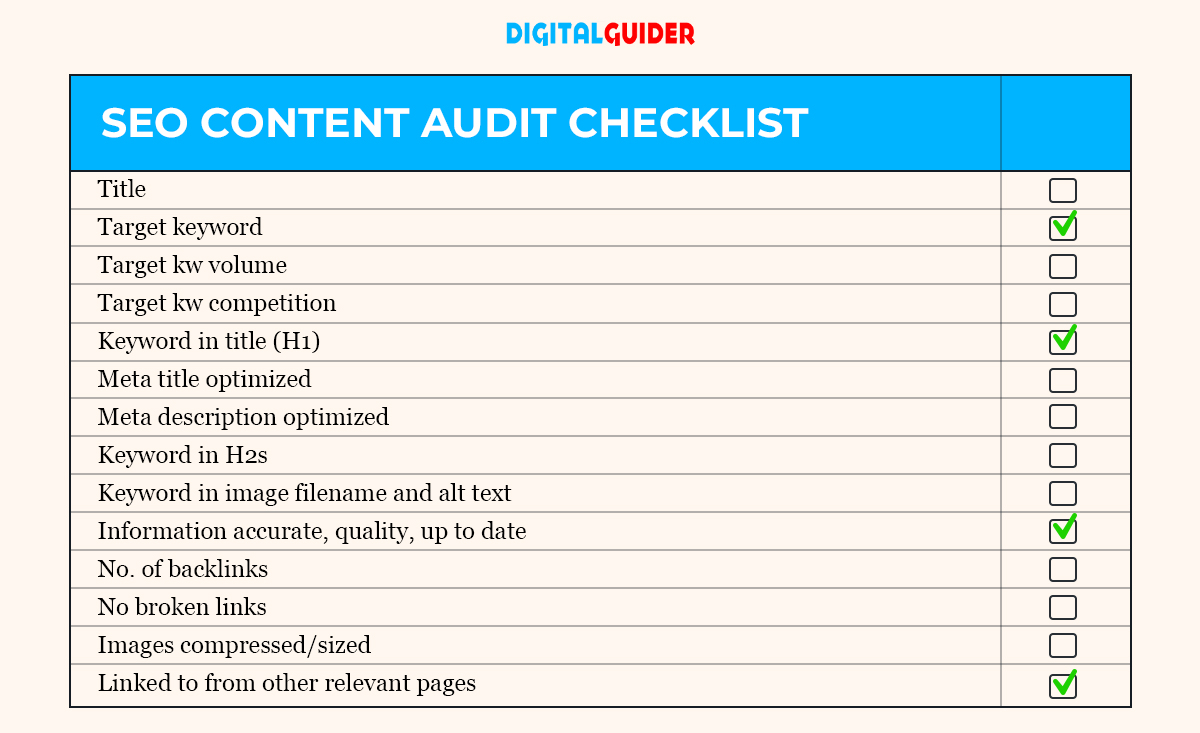
2 — Content Inspection (SEO Content Audit)
The content’s condition, quality, and age should be in check. The content should be correct and reliable so that Google can consider showing your website when users search online. Also, it should be SEO-ready.
The aim is to create content for online audiences and Google (or other search engines). The checkup on your SEO content looks at how good and relevant your content is and how well Google understands it. Go through the below diagram to understand the process of starting a Content audit.

Image credits:ahrefs
Prerequisite Tools for SEO content audit: Google Analytics, CMS, keyword research tool, Google Search Console.
Let us understand what factors should be considered when starting an SEO Content Audit.
a. Website Traffic
Look at organic traffic to prioritize pages, compare date ranges, and spot significant drops or increases. Check our SEO metrics guide for more details.
b. Keyword Targeting (On-page)
Include keywords in meta titles, meta descriptions, H1, H2s, image file names, and alt text, and avoid overloading them in the body content. Get help with on-page SEO here.
c. Meta Description and Title
Ensure keywords are front-loaded, stay within character limits, and are optimized for organic click-through rate (compelling and value-driven). Check our posts for assistance with meta descriptions and meta titles.
d. Images
Confirm there are no broken images, file names include keywords, alt text is descriptive and has keywords, and images are compressed and appropriately sized. Find guidance on Image SEO here.
e. Quality
Organize information into clear sections, ensure accuracy, keep it up to date, and make it thorough (not thin). Learn more about creating quality content here.
f. Links
Verify that links work and the page is connected to other relevant pages on your site.
g. Backlink Profile
Assess the quantity and quality of backlinks (Google Search Console can provide some information, but an SEO tool offers deeper insights).
Now comes the second significant chunk of SEO.
3 — Technical SEO Website Audit
Technical SEO helps search engines like Google locate your website and lets the bots crawl and index web pages. It provides information to let Google know it is a secure and quick website apart from being just trustworthy and reliable.

Image credits: 10web.io
Prerequisite tools for Technical Website Audit: Google Search Console, PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, Copyscape/Siteliner, SEO tool.
Technical SEO Audit Checklist
a. Indexing:
Ensure that all intended pages are indexed without errors. Check the GSC (Google Search Console) index coverage report to identify any adjustments needed in your sitemap and robots.txt files.
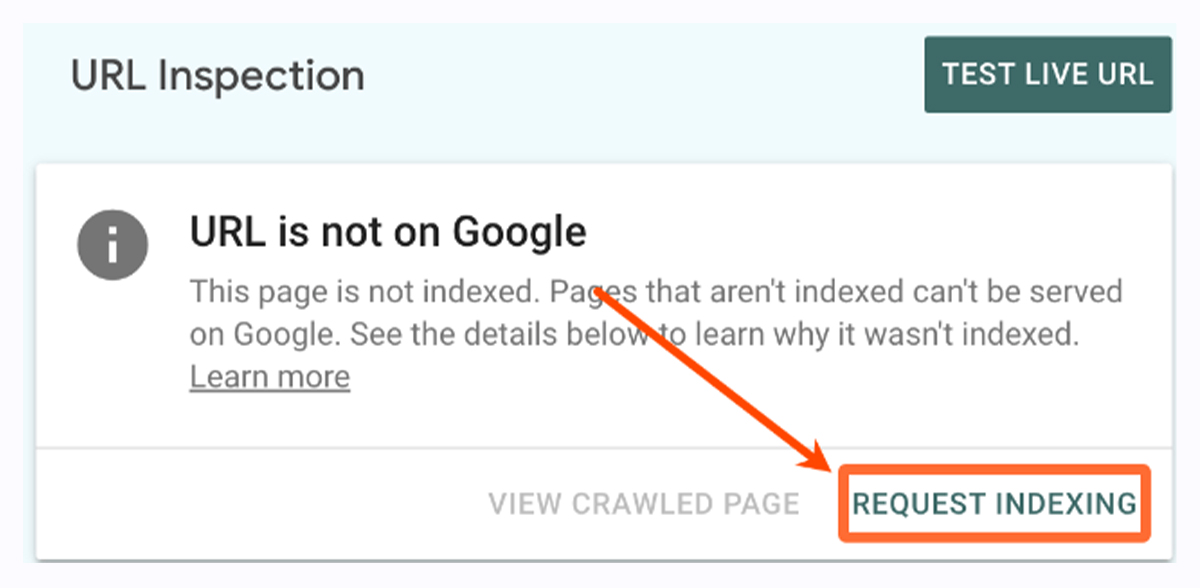
Join Google Search Console, add your website, enter your homepage in the URL Inspection tool, and click “Request indexing.” If your site structure is good (we’ll talk about that soon), Google should discover (hopefully index) all your site’s pages.
-
Sitemap
A sitemap shows Google where to locate the pages you think are crucial to your website. Find it at yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml. Include only the pages you want Google to crawl, format them correctly according to the Sitemap protocol, follow Google’s sitemap guidelines, and define their file location in robots.txt. If changes are necessary, resubmit through the GSC sitemap report. Click this link to know more.
-
Robots.txt
Access it at yourwebsite.com/robots.txt. It informs Google which pages not to crawl, is named “Robots.txt,” has only one version, follows Google’s robots.txt guidelines, and includes the sitemap’s location. If changes are made, follow instructions from your website host for resubmission.
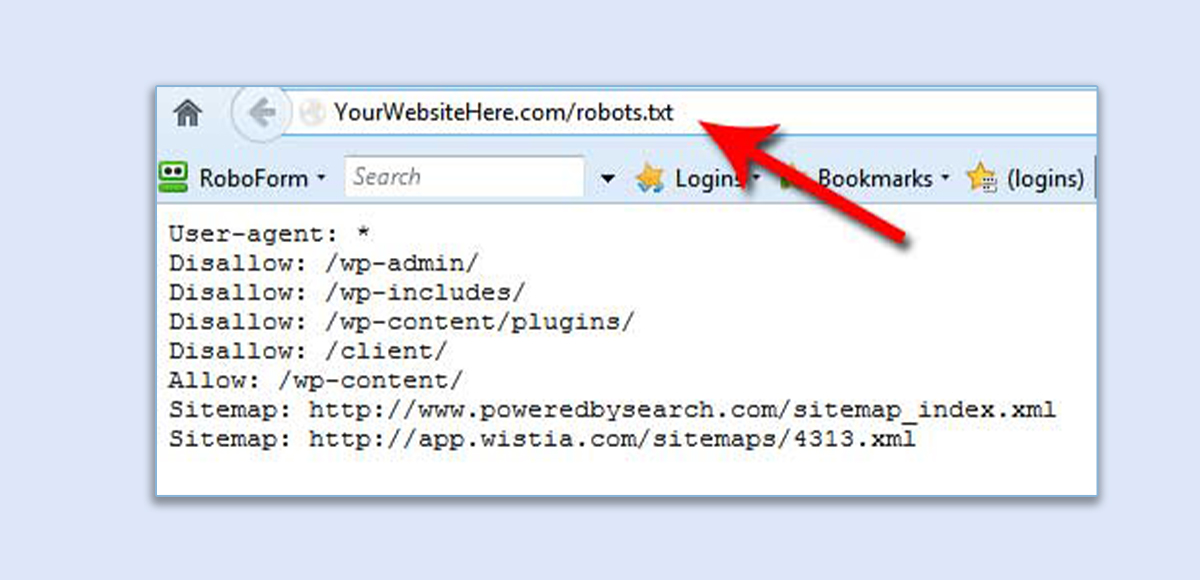
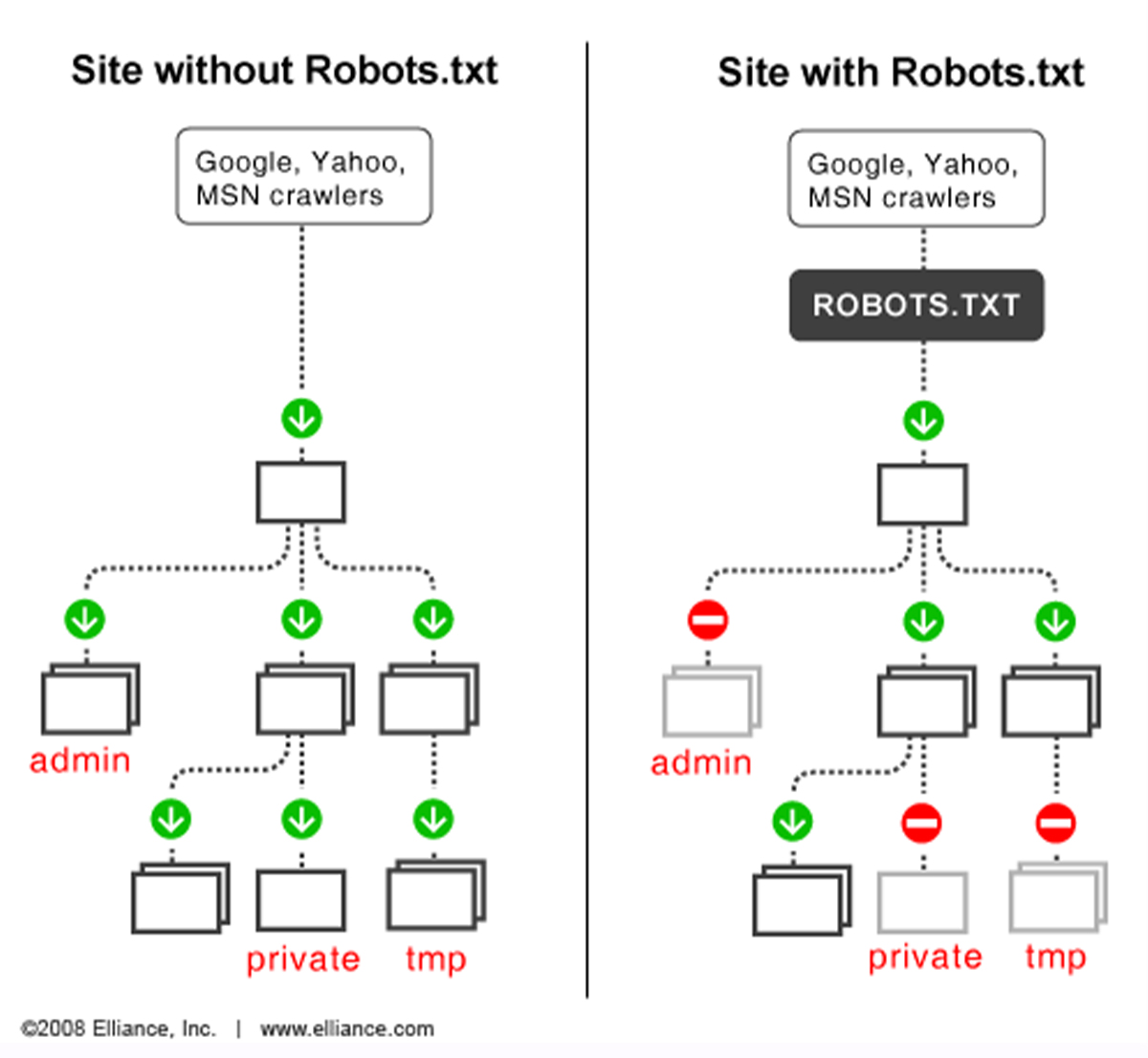
Image Credits: elliance.com
b. Core Web Vitals:
An important ranking factor covering user experience, page speed, and mobile friendliness. Audit your entire site through the GSC Core Web Vitals Report. Use Google PageSpeed Insights and Google Mobile-Friendly Test to fix identified issues. After making fixes, validate them through GSC.
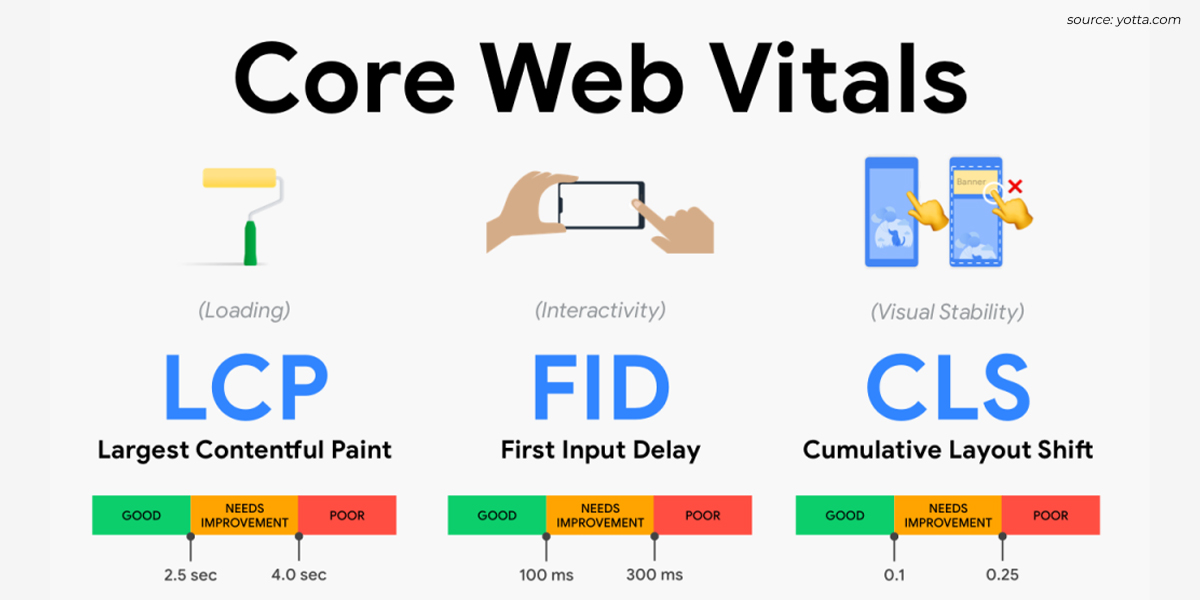
Image Credits: Yotta.com
c. Security:
Another ranking factor. Ensure your site has HTTPS (not HTTP). An SSL certificate shows crucial details to verify a website owner and secure web traffic with SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). It includes the public key, certificate issuer, and linked subdomains.
You can look for different Certificate Authorities that provide SSLs, with options ranging from less secure to more secure.
Look at the video below to learn what SSL is and how it helps.
https://youtu.be/ntVeD1sQDsg
Get Your SSL certificate:
- Check your website details with ICANN Lookup.
- Create the Certificate Signing Request (CSR). If you can get to your server, make a CSR independently. If you have cPanel through your hosting provider, use its tools for CSR generation. Or, use a free online CSR generator to skip any tricky steps.
- Send your CSR to the Certificate Authority to confirm your domain.
- Put the certificate on your website.
d. Links:
Confirm that any variations of your website address (http/https and www) redirect to the https/www domain. Redirect or remove broken links.

e. Duplicate Content:
Use Siteliner or Copyscape to identify duplicate content. Delete, redirect, or resolve with canonical tags.
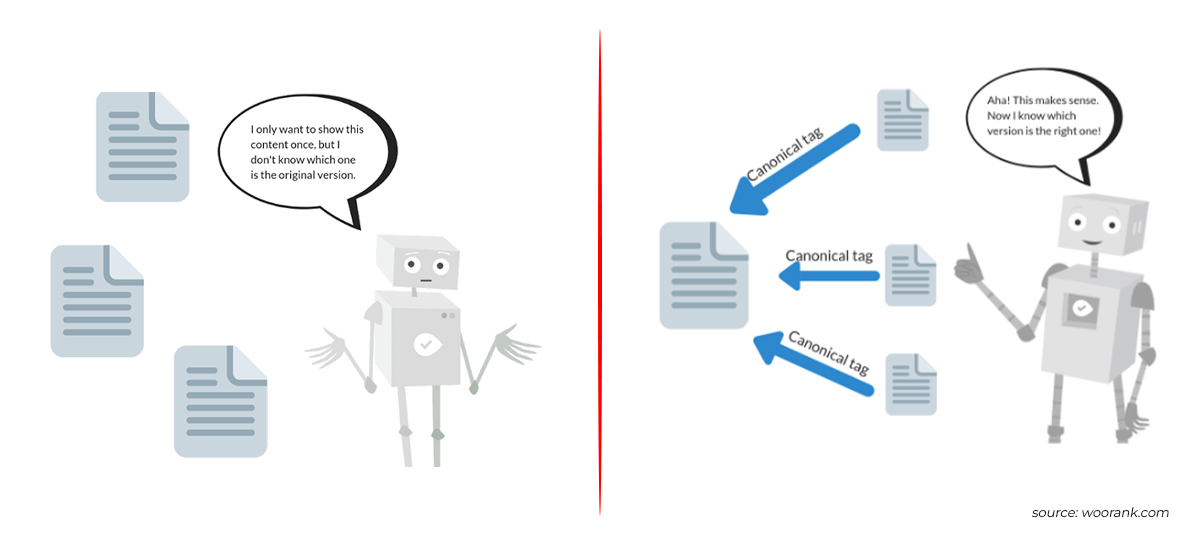
Image Credits: woorank.com
The canonical tag, or “rel canonical,” is an HTML tag that informs search engines that the URL is the page’s main and definitive version. It’s placed in the page’s <head> section and appears like this:
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com“> In simple terms, the canonical tag guides Google on which page you prefer to appear in search results.
A canonical URL is the one that search engines, such as Google, pick as the main version when there are duplicate web pages. This chosen URL is given priority to prevent repetitive content without unique value from appearing in search results.
Look at these two URLs:
Canonical URL: https://example.com/blog/
Alternate URL: https://example.com/blog/?page=1
In this case, Google will probably pick the main URL for indexing and ranking. The main page is also known as the “principal,” “primary,” or “representative” version.
f. Site Structure:
Maintain a flat architecture, allowing users and crawlers to reach any page in four clicks or less. Keep a clean and organized URL and internal linking structure.
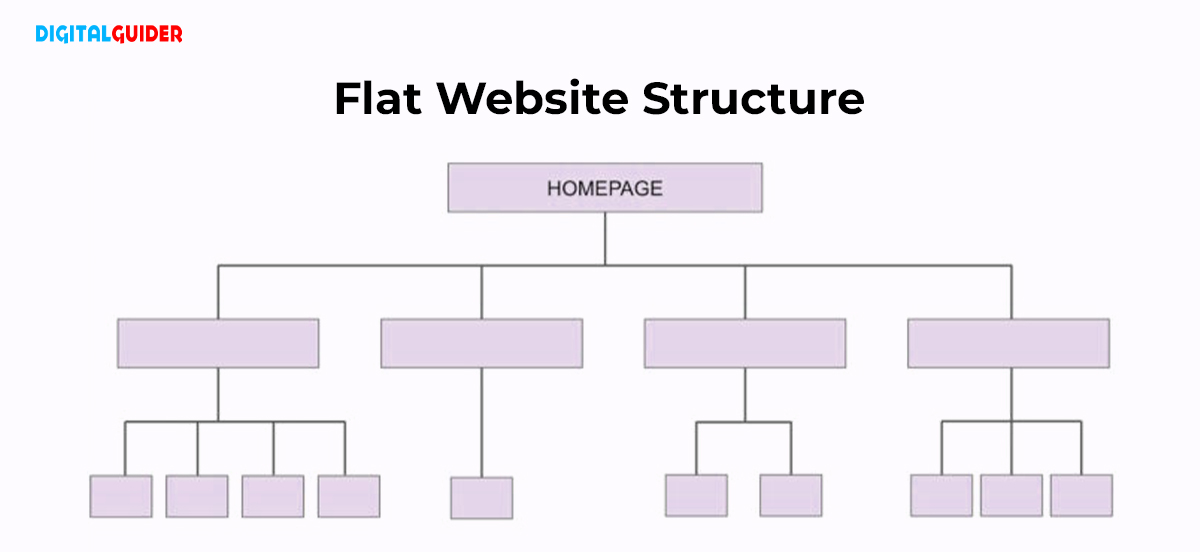
Image credits:speechsilver.com
4 — User Experience and Design
Here we will see and feel how it is to be on the website. We’ll check how the website functions and the overall picture it is giving out.
Prerequisite tools required for design audit – Content Management System, a mobile device & keen eyes.
Web Design Audit Checklist
a. Navigation
Ensure the menu is easy to use, looks the same on all pages, and uses clear labels. The logo in the header should link to the homepage, and the mobile menu should be at least 46 pixels tall.
b. Functionality
Ensure that essential actions are easy without obstacles and that repetitive tasks are simple.
c. Forms
Clearly, label fields, show errors before submission, and provide a success message after completion.
d. Text
Use two or fewer font styles, and ensure fonts are readable in all formats (like all caps, italics, bold). Keep font sizes and styles consistent throughout the site.
e. Visual design
Prioritize important information, use elements other than color to show meaning and function, leave space around essential items, ensure clear contrast between foreground and background elements, follow existing design patterns, and have a favicon for your logo in browser tabs.
f. Perception
Users should quickly understand your industry and product/service, find essential information quickly, perform actions without difficulty, and understand where buttons and links will take them. Each page’s intended action should be explicit, and your brand’s look and feel should be consistent across the site.
Website Accessibility Audit
This is for people with disabilities. This website check looks at visual and hearing issues, but a complete accessibility review should include everything, like epilepsy, learning disabilities, cognitive challenges, and more.
Prerequisites: Accessibility tools and a mobile device.
You can find a complete list of accessibility tools and checklists on W3.org and Wave.
https://youtu.be/ITUDiTgAZY0
Web Accessibility Audit Checklist
a. Text
Use HTML tags for titles, headings, subheadings, lists, and call-out text. Make sure the text in the body is at least 16px (better if it’s 18px) and has a contrast ratio 4:5:1. Large text should be at least 24px. The bold and linked text needs a contrast ratio of at least 3:1. Maintain a line spacing of at least 1.5. Make anchor text clear and descriptive. Allow users to enlarge or reduce text size.
b. Image, video, audio
Provide detailed alt text for images and subtitles or transcripts for audio and video. Users should be able to pause, mute, or exit auto-played content. If images include tables or text, make sure the actual tables and text are also present.
c. Usability
Ensure users can navigate and use the site with only a keyboard. Page titles should be clear and descriptive. Maintain the same menu order throughout the site and avoid imposing time limits.
5 — Website CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization) Audit
Website CRO Audit involves boosting the percentage of users or visitors on your website who perform a specific action, aiming to increase the number of leads you get.
This is done by improving content, conducting split tests, and enhancing workflows. The outcome of conversion rate optimization includes more high-quality leads, higher revenue, and reduced customer acquisition costs.
Prerequisites: CRM (Customer Relationship Management), Mobile Device, SEO software.
Website CRO Audit Checklist
a. CTA
Make the Call-to-Action (CTA) stand out on the homepage with clear buttons that look like buttons. Use color contrast, size, whitespace, and directional cues. Ensure the CTA is visible without scrolling (best practices for CTAs apply).

Image Credits: wyzowl.com
b. Copywriting
Write descriptive and appealing text for the CTA. Keep page copy clear, concise, and conversational, avoiding excessive sales language. Communicate value and trust in your content (tips on writing convincing copy here).
c. Page Design
Keep the page design organized, avoid clutter, and include sufficient whitespace for a visually appealing look.
d. SEO
Ensure gated content is not indexed. Optimize important pages for both content and technical SEO.
e. Landing Pages
Check if landing pages are indexed as intended. Have only one clear CTA on each landing page. Keep the landing page consistent with the preceding ad or offer (best practices for landing pages apply).
f. Forms
Clearly label and organize forms with minimal fields. Identify errors before submission. Show a thank-you message or an optimized thank-you page after submission. Ensure information syncs with CRM and other automation tools, and provide users with the promised offer.
g. Popups/Chat
Make sure popups and chat features only appear on intended pages.
h. Mobile
Ensure everything works smoothly on mobile devices.
Conclusion
We hope you have gone through all the points and that it will help you conduct a full-fledged website audit for your business website. Doing a complete website audit requires time. Once you’ve collected the information outlined in this guide, deciding which website improvements to focus on can be challenging.
We suggest doing an SEO content audit every three to six months, depending on your business requirements. Make sure to allow sufficient time between each audit cycle so that any changes can show results before starting the next audit.
In case you have planned a website redesign for the future, contact us at +1-307-209-3608 or send us an email at [email protected].
The post How to Audit Your Website for SEO? appeared first on DigitalGuider.
Source: digitalguider.com